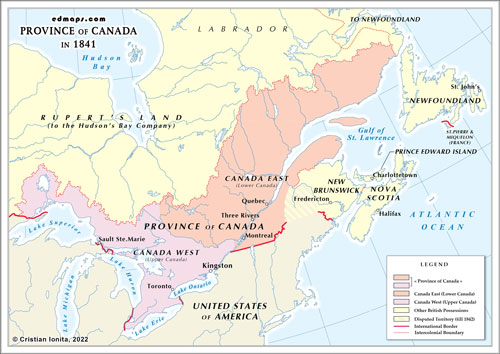
Province of Canada in 1841


The Province of Canada in 1841
Before the Act of Union of 1840, the territory that would eventually become Province of Canada was divided into two separate entities: Upper Canada and Lower Canada.
Upper Canada, also known as Canada West, encompassed the region that is now the southern part of the province of Ontario. It was primarily English-speaking and had a predominantly British population. The capital of Upper Canada was Toronto (known as York until 1834).
Lower Canada, also known as Canada East, covered the region that is now the southern part of the province of Quebec. It had a predominantly French-speaking population and retained strong ties to French culture and traditions. The capital of Lower Canada was Quebec City.
The division between Upper Canada and Lower Canada was established by the Constitutional Act of 1791. The act was implemented to address the cultural and linguistic differences between the English-speaking and French-speaking populations in the region.
However, in 1840, the Act of Union was passed by the British Parliament, which united Upper Canada and Lower Canada into a single entity known as the United Province of Canada. The Act of Union took effect on February 10, 1841, and established a centralized government for the newly formed province. The goal of the union was to reconcile the tensions between the English and French populations and create a more efficient and stable administration.
The United Province of Canada was further divided into two regions: Canada East (formerly Lower Canada) and Canada West (formerly Upper Canada). This division allowed for some degree of representation and autonomy for each region within the united entity.
It's worth noting that the provinces of Nova Scotia and New Brunswick, located in the Atlantic region of present-day Canada, were separate entities during this time and were not part of the United Province of Canada. The process of confederation, which led to the creation of the Dominion of Canada in 1867, involved the inclusion of additional provinces and the expansion of the country's territorial boundaries.