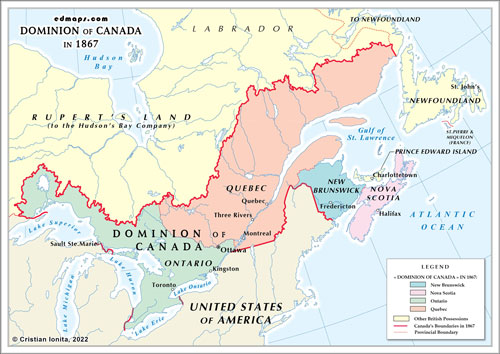
Dominion of Canada in 1867


Dominion of Canada in 1867
When the Dominion of Canada was established in 1867 through the enactment of the Constitution Act, 1867 (formerly known as the British North America Act, 1867), it consisted of the following provinces:
Ontario: Situated in the western part of the Dominion, Ontario extended from the western border of Quebec to the Great Lakes. It included cities such as Toronto and Ottawa, the Dominion's capital.
Quebec: Located to the east of Ontario, Quebec covered a large portion of eastern Canada. It stretched from the northeastern border of Ontario to the eastern coast and included cities like Montreal and Quebec City.
New Brunswick: Positioned on the eastern coast of Canada, New Brunswick was northeast of Maine (United States). It bordered Quebec to the northwest and Nova Scotia to the southeast. Major cities in New Brunswick included Fredericton and Saint John.
Nova Scotia: Situated in the Atlantic region of Canada, Nova Scotia was a peninsula that jutted out into the Atlantic Ocean. It was southeast of New Brunswick and had major cities such as Halifax.
These four provinces formed the initial core of the Dominion of Canada at its creation in 1867. The Dominion of Canada was a federal parliamentary democracy that united these provinces under a central government.
It's important to note that at the time of Confederation in 1867, the western territories such as Manitoba, British Columbia, and the Northwest Territories were not part of the Dominion of Canada. These territories were incorporated into the Dominion through subsequent expansions and negotiations in the years following 1867.