Dominion of Canada in 1871


Dominion of Canada in 1871
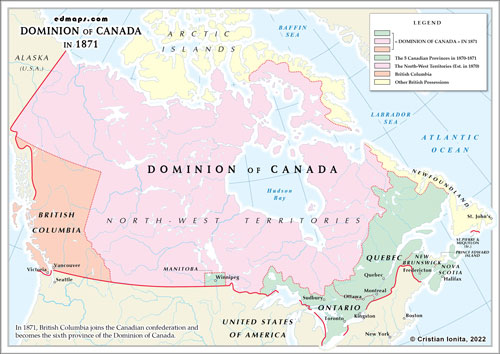
By 1871, the Dominion of Canada had expanded its territorial boundaries from the four original provinces (Ontario, Quebec, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia) and had annexed other two provinces (Manitoba and British Columbia) and two territories (Rupert's Land and the Northwestern Territory) . Here's a description of the Dominion's divisions and their general locations:
Ontario: Situated in east-central Canada, Ontario extended from the western border of Quebec to the northern shores of the Great Lakes. It included cities such as Toronto, Ottawa, and Kingston.
Quebec: Located to the east of Ontario, Quebec covered a large portion of eastern Canada. It stretched from the northeastern border of Ontario to the eastern coast and included cities like Montreal and Quebec City.
New Brunswick: Positioned on the eastern coast of Canada, New Brunswick was northeast of Maine, United States. It bordered Quebec to the northwest and Nova Scotia to the southeast. Major cities in New Brunswick included Fredericton and Saint John.
Nova Scotia: Situated in the Atlantic region of Canada, Nova Scotia was a peninsula that jutted out into the Atlantic Ocean. It was southeast of New Brunswick and had major cities such as Halifax.
Manitoba: Located west of Ontario, Manitoba was a new province that was established in 1870. It encompassed the region surrounding the Red River and Winnipeg.
British Columbia: Situated on the western coast of Canada, British Columbia was a separate colony until it joined the Dominion of Canada in 1871. It extended from the Rocky Mountains to the Pacific Ocean and included cities such as Victoria and Vancouver.
Rupert's Land and the North-Western Territory were combined under the new name of the North-West Territories in 1870.